
Sparwood is a district municipality in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is the second-largest community on the Elk River.

A dump truck, known also as a dumping truck, dump trailer, dumper trailer, dump lorry or dumper lorry or a dumper for short, is used for transporting materials for construction as well as coal. A typical dump truck is equipped with an open-box bed, which is hinged at the rear and equipped with hydraulic rams to lift the front, allowing the material in the bed to be deposited ("dumped") on the ground behind the truck at the site of delivery. In the UK, Australia, South Africa and India the term applies to off-road construction plants only and the road vehicle is known as a rat lorry, tipper lorry, tipper truck, tip truck, tip trailer or tipper trailer or simply a tipper.

The Liebherr T 282 series are off-highway, ultra class, rigid frame, two axle, diesel-electric, AC powertrain haul trucks designed and manufactured in the United States by Liebherr Mining Equipment Co.

The EMD F2 was a freight-hauling diesel locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division between July 1946 and November 1946. It succeeded the FT model in GM-EMD's F-unit sequence, and was replaced in turn by the F3. The F2 was in many respects a transitional type between those two; it kept the 1,350 hp (1,010 kW) rated D8 generator from the FT due to late development of the new D12 generator intended for the F3, but in a revised carbody design and internal layout that would be continued through the rest of the F-unit series. 74 cab-equipped lead A units and 30 cabless booster B units were produced.

EMD F-units are a line of diesel-electric locomotives produced between November 1939 and November 1960 by General Motors Electro-Motive Division and General Motors-Diesel Division. Final assembly for all F-units was at the GM-EMD plant at La Grange, Illinois, and the GMDD plant in London, Ontario. They were sold to railroads throughout the United States, Canada and Mexico, and a few were exported to Saudi Arabia. The term F-unit refers to the model numbers given to each successive type, all of which began with the letter F. The F originally meant "fourteen", as in 1,400 horsepower (1,000 kW), not "freight". Longer EMD E-units for passenger service had twin 900-horsepower (670 kW) diesel engines. The E meant "eighteen" as in 1,800 horsepower (1,300 kW). Similarly, for early model EMD switchers, S meant "six hundred" and N meant "nine hundred horsepower".

The EMD FP9 is an American 1,750 horsepower (1,300 kW), B-B dual-service passenger and freight-hauling diesel locomotive that was produced between February 1954 and December 1959 by General Motors Electro-Motive Division, and General Motors Diesel. Final assembly was at GM-EMD's La Grange, Illinois plant, except for Canadian orders, which were assembled by Canadian subsidiary GMD at London, Ontario. The FP9 was essentially EMD's F9 locomotive extended by 4 feet (1.2 m) to give greater steam generator and water capacity for hauling passenger trains. A total of 90 cab-equipped lead A units were built; unlike the freight series, no cabless booster B units were sold. Regular F9B units were sometimes used with FP9 A units, since they, lacking cabs, had more room for water and steam generators. The FP9 and its predecessor, the FP7, were offshoots of GM-EMD's highly successful F-unit series of cab unit diesel locomotives.

The Caterpillar D11T is a large bulldozer, manufactured by Caterpillar Inc. in East Peoria, Illinois, and mainly used in the mining industry. Primarily designed as a bulldozer, it is also used for push-loading scrapers, and ripping rock overburden.

The Caterpillar 797 is a series of off-highway, ultra class, two-axle, mechanical powertrain haul trucks developed and manufactured in the United States by Caterpillar Inc. specifically for high-production mining and heavy construction applications worldwide. In production since 1998, the 797 series represents Caterpillar’s largest, highest capacity haul trucks. The current, third-generation model, the 797F, offers one of the largest haul truck payload capacities in the world, up to 400 short tons (363 t) and has the highest payload capacity among mechanical drive haul trucks.

Bucyrus-Erie was an American surface and underground mining equipment company. It was founded as Bucyrus Foundry and Manufacturing Company in Bucyrus, Ohio, in 1880. Bucyrus moved its headquarters to South Milwaukee, Wisconsin in 1893. In 1927, Bucyrus merged with the Erie Steam Shovel Company to form Bucyrus-Erie. In 1997, it was renamed Bucyrus International, Inc.. In 2010 the enterprise was purchased by Caterpillar in a US$7.6 billion transaction that closed on July 8, 2011. At the time of its acquisition, the Bucyrus product line included a range of material removal and material handling products used in both surface and underground mining.
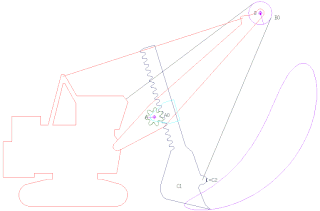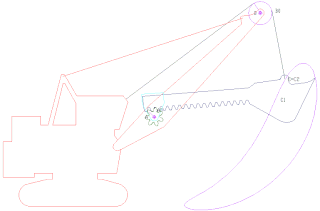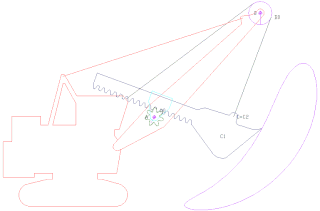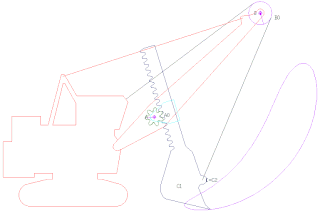
A power shovel, also known as a motor shovel, stripping shovel, front shovel, mining shovel or rope shovel, is a bucket-equipped machine usually powered by steam, diesel fuel, gasoline or electricity and used for digging and loading earth or fragmented rock and for mineral extraction. Power shovels are a type of rope/cable excavator, where the digging arm is controlled and powered by winches and steel ropes, rather than hydraulics like in the modern hydraulic excavators. Basic parts of a power shovel include the track system, cabin, cables, rack, stick, boom foot-pin, saddle block, boom, boom point sheaves and bucket. The size of bucket varies from 0.73 to 53 cubic meters.

Terex Corporation is an American company and worldwide manufacturer of lifting and material-handling equipment. The company works within a variety of industries including construction, infrastructure, quarrying, recycling, energy, mining, shipping, transportation, refining, and utilities. The company is well known for producing heavy machinery.

The Euclid Company of Ohio was a manufacturer which specialized in heavy equipment for earthmoving, particularly dump trucks, loaders and wheel tractor-scrapers. It operated in the US from the 1920s to the 1950s, when it was purchased by General Motors. The firm was later bought by Hitachi Construction Machinery.

The Komatsu 930E is an off-highway, ultra class, rigid frame, two-axle, diesel/AC electric powertrain haul truck designed and manufactured by Komatsu in Peoria, Illinois, United States. Although the 930E is neither Komatsu's largest nor highest payload capacity haul truck, Komatsu considers the 930E to be the flagship of their haul truck product line.

Haul trucks are off-highway, rigid dump trucks specifically engineered for use in high-production mining and heavy-duty construction environments. Haul trucks are also used for transporting construction equipment from job site to job site. Some are multi-axle in order to support the equipment that is being hauled.
The DAC 120 DE is a diesel-electric haul truck manufactured between 1988 and 1990 by Steagul Roșu Brașov Romania and by Mecanica Mârşa Works.
The Bucyrus MT6300AC is an off-highway, ultra class, two-axle, diesel/AC electric powertrain haul truck designed and manufactured by Bucyrus International Inc. in the United States. The MT6300AC is Bucyrus' largest, highest payload capacity haul truck, offering one of the largest haul truck payload capacities in the world, up to 400 short tons (363 t). The closest analogs are Liebherr T 282B, Caterpillar 797F, which can carry the same weight, and BelAZ 75710 with 450 tons payload capacity.
The Komatsu 960E-1 (960E) is an off-highway, ultra-class, rigid-frame, two-axle, diesel/AC electric powertrain haul truck designed and manufactured by Komatsu in Peoria, Illinois, United States. The 960E-1 has been Komatsu's largest, highest capacity haul truck, offering a payload capacity of up to 360 short tons (327 t). The 960-E1 is the first generation of the 960E series of haul trucks and is alternately referred to by Komatsu specifically as the 960E-1 or generally as the 960E.

Unit Rig was a manufacturer of haul trucks, sold under the brand name Lectra Haul.
The Payhauler is a series of dump trucks that were produced from 1956 to 2003. Introduced by International Harvester as the International Harvester Payhauler, the line was spun off in 1982 into a separate company, the Payhauler Corporation.

Dart was a manufacturer of commercial vehicles in Waterloo, Iowa, that was established around 1910.

















